Docker On Windows Real Quick

You’ve got a Windows computer. You want to know what the deal with Docker is.
You don’t wanna read a whole lot.
Here’s how you start.
Step 1: Download
Download Docker Toolbox from the following link.
https://www.docker.com/products/docker-toolbox
Step 2: Install
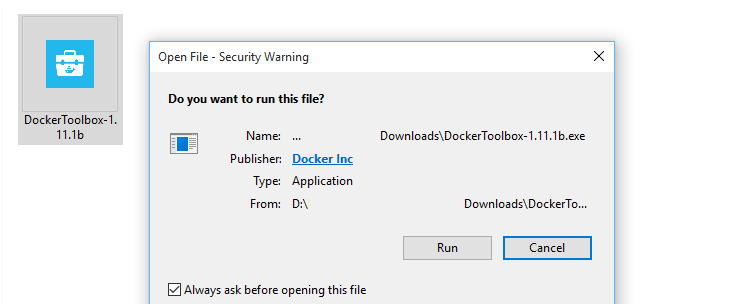
Double click the executable and leave all the default options checked.
This will install Docker, the Docker Quickstart Terminal, Kitematic and a variety of other tools Docker uses.
Step 3: Run Quickstart Terminal
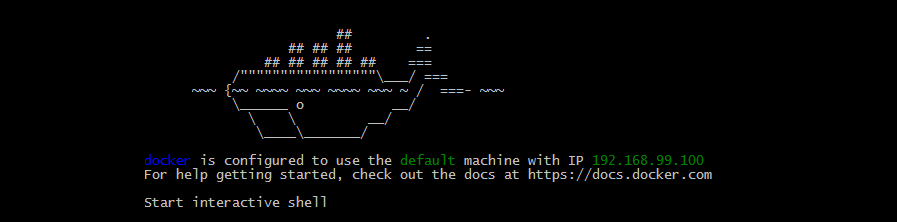
After the install, run the quickstart terminal. If you see an ASCII whale, you’re in the clear.
Make a note the IP address it provides. It is important.
Step 4: Run Kitematic & Select a Container
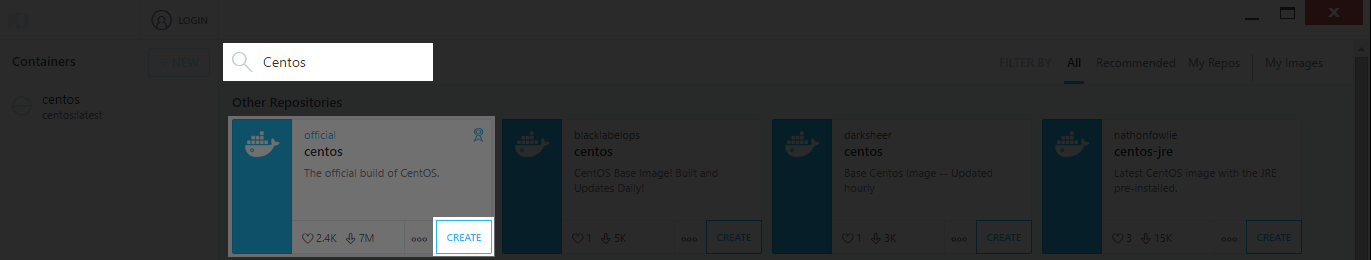
Run Kitematic. From here you can add & run any container environment with ease.
As an example I will add a new CentOS box. All I need to do is search for “Centos”, and click the “Create” button on the repository I have chosen.
This will download and install the image, and add a new entry to my list of containers.
Step 5: Run The Container & Connect to Docker
The container should have started automatically after installation. If it didn’t, you can select it and press the “Start” button in Kitematic, or you can wait until after you have connected to the VM.
To proceed, you can use either an SSH client like PuTTY, or just use the Docker Quickstart Terminal.
If you’d just like to use the Quickstart Terminal, proceed to Step 6.
If you’d like to use SSH, once the machine is set up and running, SSH into the Docker VM with the IP address provided earlier, using PuTTY or another SSH client.
DEFAULT LOGIN CREDENTIALS
Username: docker
Password: tcuser
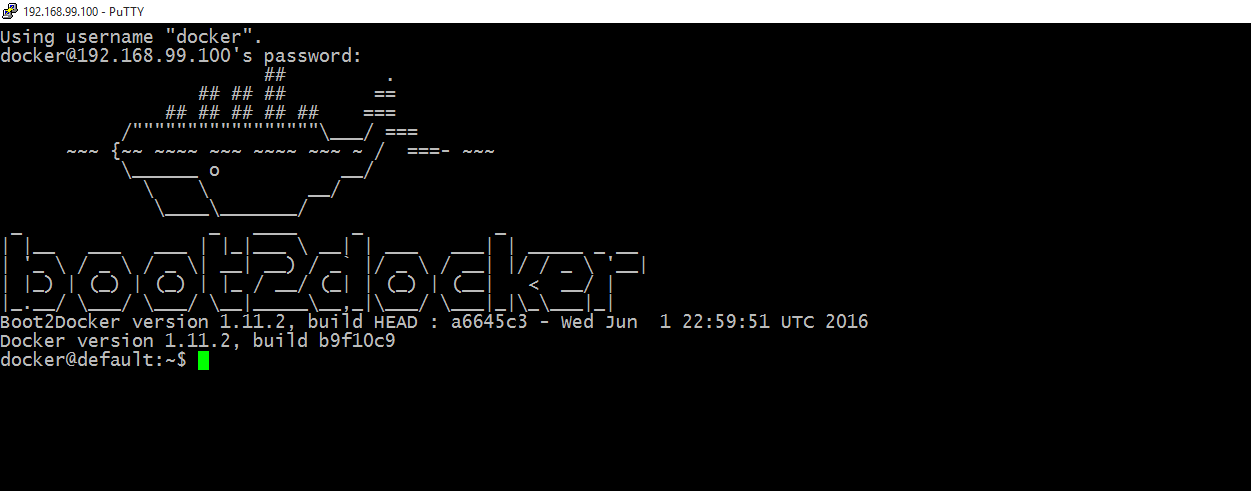
Step 6: Attach Your Session
You’re currently in the Boot2Docker VM. You can choose and attach your session to any of your containers from here.
Here are some useful commands to know
docker ps // Shows all running containers
docker start <name> // Starts the container named <name>
docker attach <name> // Attaches your session to the container <name>
Type docker attach centos to attach the session to the container.
Your session should look something like this.
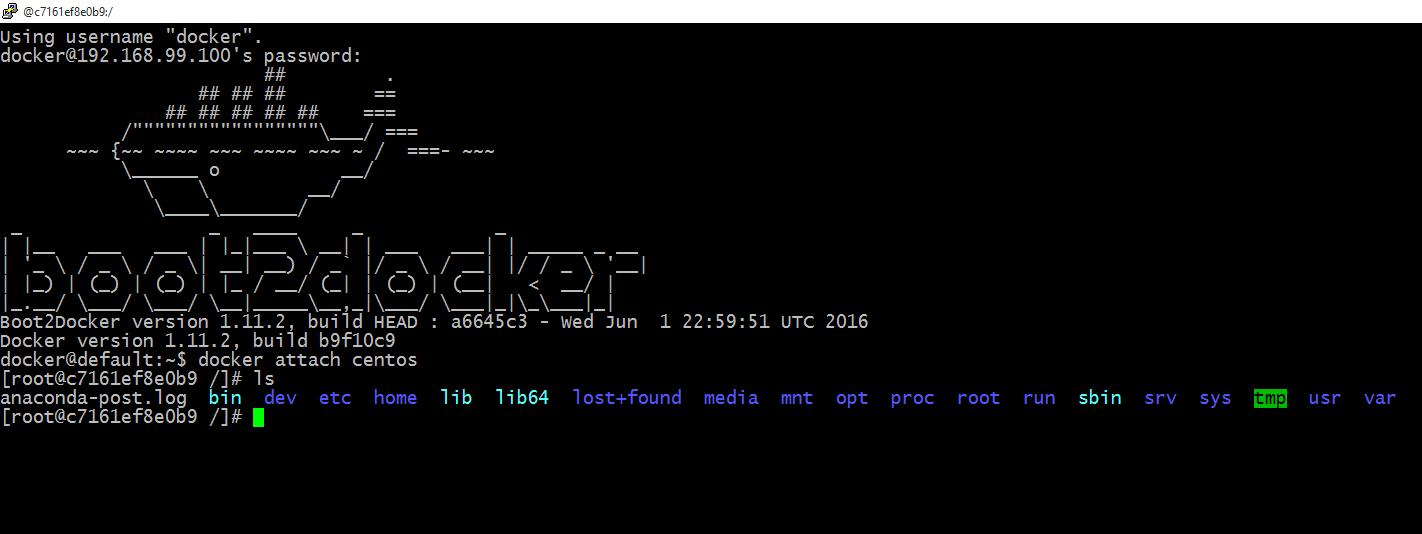
And That’s Literally It.
You are connected to your environment.
That took all of what? 5 minutes?
Here’s a link to the Docker Command Line API if you’d like a comprehensive list of commands.